



CYFIRMA research team has observed impersonated web download pages of Zoom Application – which is the most downloaded application in recent years. We believe with moderate confidence that financially motivated FIN11 is behind this campaign. This threat actor is known for conducting a large-scale campaign using the impersonated web applications. In this case, FIN 11 was observed employing Zoom download pages to install Information Stealer (Vidar) targeting a large attack surface. We also observed an IP address that was earlier associated with AsyncRAT.
As per our VT research, the threat actor is using the disguised Zoom application which is used worldwide as a video conference solution indicating its focus to compromise a large number of systems across all operating systems using popular web applications. Russia-based threat actor FIN11 has lately been associated with CLOP ransomware for post-compromise ransomware deployment and data theft extortion. This association with the ransomware group increases the possibility of compromised systems becoming potential ransomware victims.
Several fake Zoom Video Communications download pages were discovered in the wild by the CYFIRMA research team. The Russian Federation is the registrant country for all the hosts. The CYFIRMA research team believes with moderate confidence that financially motivated FIN11 is behind this campaign involving fake download pages of popular web applications used worldwide.
Below are the six impersonated web application download page links observed in the wild.
During our passive DNS research, we observed a vast number of impersonated web applications used in the past. Here are a few sample links:
The Zoom Video Communication application as a phishing lure has been historically been used in large-scale campaigns. Since, the past two years, due to COVID-19, the world saw a significant increase in remote work, distance education, as well as the growth of online social relations. This led to high downloads of the Zoom application, and the trend has continued even after the pandemic. Zoom emerged as one of the most downloaded applications in the world year after year. For instance, with 300 million downloads, it was the most downloaded business app worldwide in 2021.
This popularity of Zoom has led to a renewed interest in employing it as phishing lures. In the reported incident, the threat actor employed the ‘Vidar’ information stealer embedded in the Zoom application to target broad attack surface across all industries and geographies.

Since 2016, the Russian-based threat actor group FIN11 has been conducting widespread phishing campaigns. Initially, the threat group targeted financial, retail, and hospitality organizations. However, FIN11 later broadened its target to include a diverse set of sectors and geographic regions. During their phishing operations, threat actors cast a wide net and then select which victims to further exploit based on characteristics such as sector, geolocation, or perceived security posture. FIN11 has lately been associated with CLOP ransomware for post-compromise ransomware deployment and data theft extortion. Historically, the group has used services that provide anonymous domain registration, bulletproof hosting, code signing certificates, and private or semi-private malware; this strategy has been carried over into the ongoing campaign. In this incident, the threat actor used Vidar information stealer which is one of the prominent malware used by the group.
The observed hosts (six links mentioned above) are pointed to malicious .exe, .rar, .apk, .lnk, and .pdf files indicating that a well-planned campaign by FIN 11, targets all operating systems to compromise a large attack surface.
Details are shared below.
https://zoom-download[.]host – 92[.]53[.]96[.]41
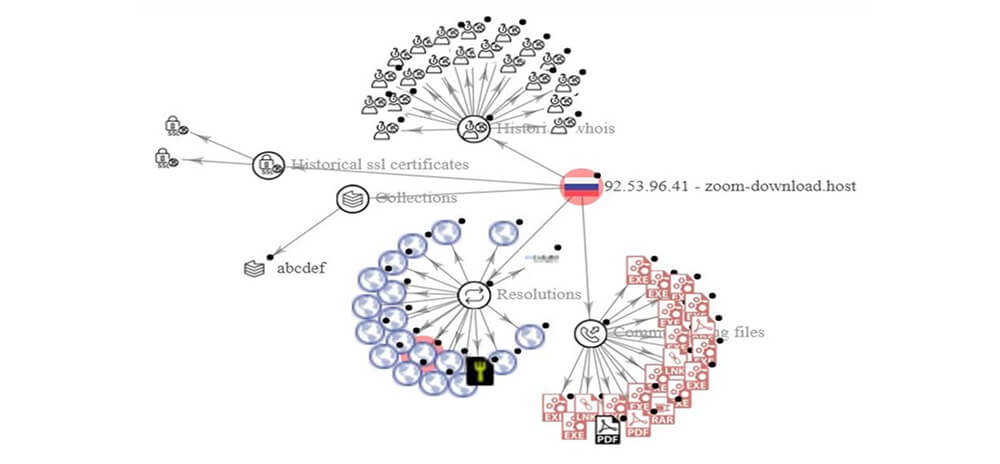
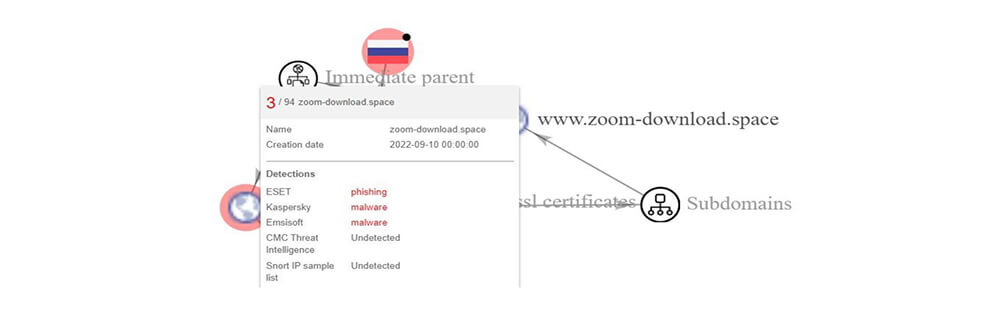
https://zoom-download[.]space – 2a03:6f00:1::5c35:6029
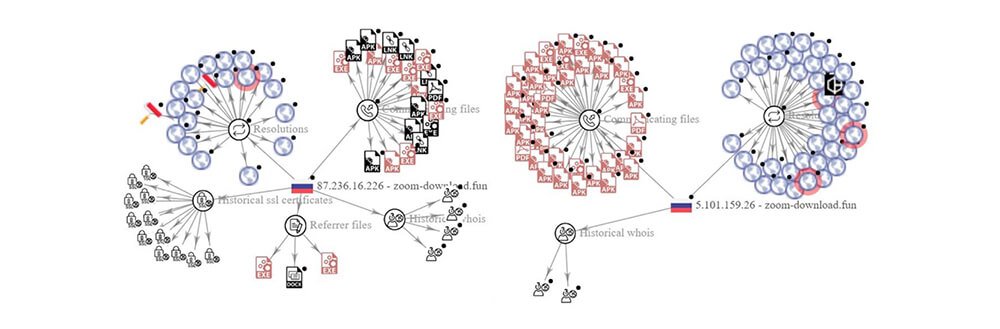
https://zoom-download[.]fun – 92[.]53[.]96[.]41 pDNS – 5[.]101[.]159[.]26; 87[.]236[.]16[.]226
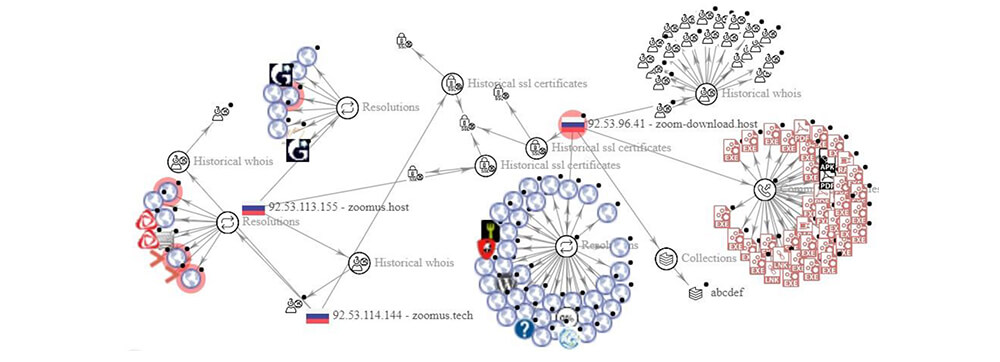
https://zoomus.host – 92[.]53[.]113[.]155; https://zoomus.tech – 92[.]53[.]114[.]144
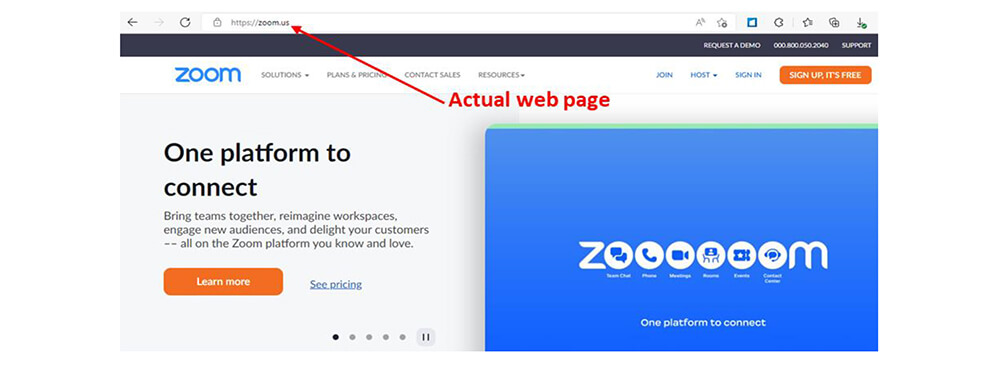

Our research team analysed samples obtained from impersonated Zoom application download page. When clicked on the Download button, a malicious zip archive (8B07C2E1D99A6E43FB29C4B1A23BC743) downloaded which contains malicious “Zoom.exe” (19AFF3D6ED110A9037AFF507CAC4077F) file pretends to be a legitimate Zoom App having a Zoom icon. This file “Zoom.exe” is a 64-bit SFX [Microsoft Cabinet] file. Once extracted “Zoom.exe”, it contains two files: “ZOOMIN~1.EXE” (E710423F15A7C40DAC815C2D637CABD0) which is zoom application setup [legitimate], 2nd one is “Decoder.exe” (98C8C28B790BBCE2BC2F20CC8FF2BD8E) which is a malicious downloader.
Upon execution “Zoom.exe”, it drops “Decoder.exe” and “ZOOMIN~1.EXE” at location “C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Temp\IXP000.TMP\“. “Decoder.exe” (as mentioned above- 98C8C28B790BBCE2BC2F20CC8FF2BD8E), is a malicious downloader and “ZOOMIN~1.EXE” (as mentioned above-E710423F15A7C40DAC815C2D637CABD0) is a valid zoom installer which installs the legitimate zoom app on the system so that the execution does not create suspicion to the user.
Following is the process tree corresponding to the execution of malicious “Zoom.exe”:

The “Decoder.exe” when executed, establishes a connection with “hxxp[:]//193[.]106[.]191[.]223/CharSequence[.]TextPaint[.]setAlignment.module8_Rkbbnqyt[.]png” and downloads an encoded .PNG (21ABAC012CAA151DA5ED7C760198FAC6) file.
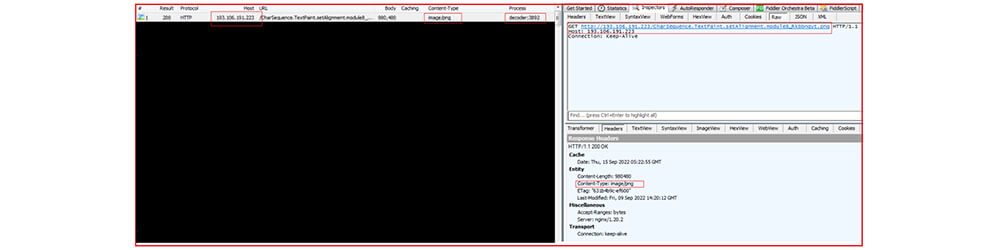
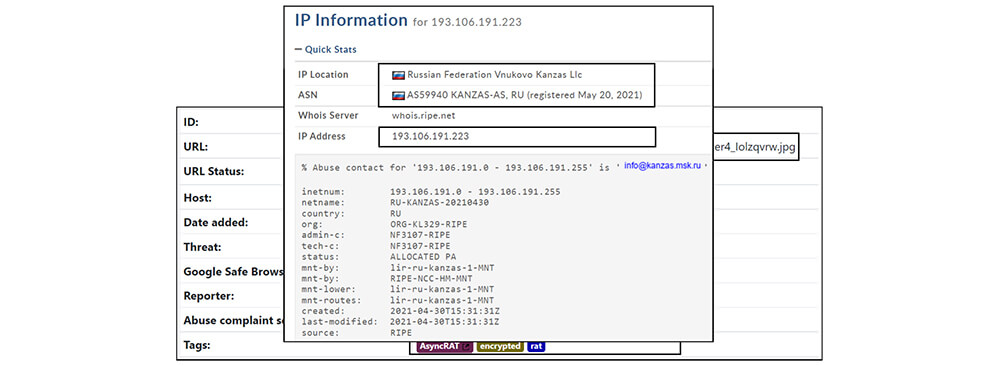
The IP address (193[.]106[.]191[.]223) is attributed to Russia and with AsyncRAT as shown below :
Later, “Decoder.exe” leverage PowerShell and execute Base64 encoded command as shown below:
“C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe” -enc UwB0AGEAcgB0AC0AUwBsAGUAZQBwACAALQBTAGUAYwBvAG4AZABzACAAMQAyAA==
The Base64 encoded command:
“UwB0AGEAcgB0AC0AUwBsAGUAZQBwACAALQBTAGUAYwBvAG4AZABzACAAMQAyAA==” when decoded equivalent to “S t a r t-Sleep-Seconds 12” might be used to become inactive for 12 seconds before next operation.
Further, it creates a child process with the name MSBuild.exe. The Microsoft Build Engine (MSBuild.exe) is a platform for building applications. This engine, which is also known as MSBuild, provides an XML schema for a project file that controls how the build platform processes and builds software. Visual Studio uses MSBuild, but MSBuild does not depend on Visual Studio. By invoking msbuild.exe on a project or solution file, we can orchestrate and build products in environments where Visual Studio is not installed. The malware authors earlier also in several instances abused the Microsoft Build Engine (MSBuild) to deploy remote access tools (RATs) and password-stealing malware.
The first stage (Decoder.exe) is a simple .NET downloader that will execute a second-stage payload in memory. The downloaded second-stage payload injects inside another process (MSBuild.exe).
The compromised MsBuild.exe make a connection with IP (116[.]202[.]179[.]139) and later download the zip file:
hxxp[:]//116[.]202[.]179[.]139/1547 hxxp[:]//116[.]202[.]179[.]139/9642742070[.]zip
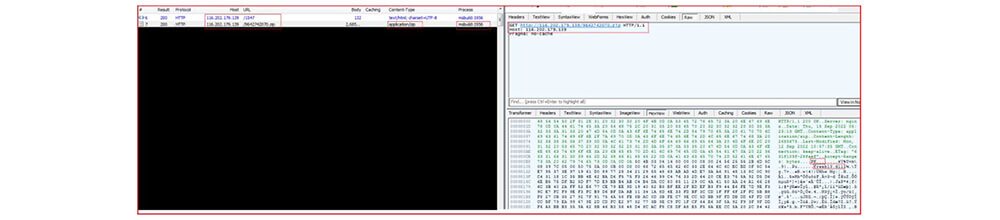
At a different running instance, the MsBuild.exe make a connection with another IP (79[.]124[.]78[.]206) and further download a similar zip file:
hxxp://79[.]124[.]78[.]206/1547
hxxp://79[.]124[.]78[.]206/1317434164[.]zip
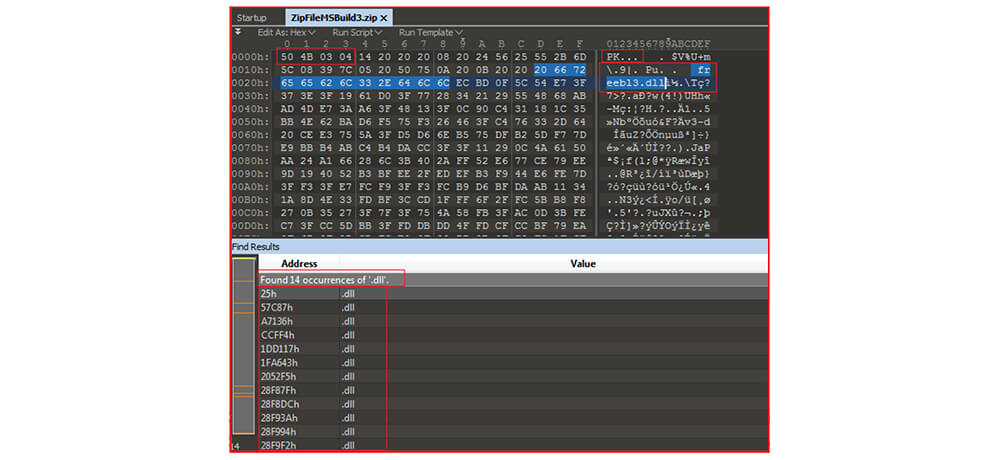
The downloaded zip file contains a series of DLL files:
“Freebl3.dll, mozglue.dll, msvcp140.dll, nss3.dll, softokn3.dll, vcruntime140.dll” In the past same set of DLLs were used by information Stealer malware – “Vidar”
The threat actor delivers malicious Zoom applications through phishing URLs masquerading as legitimate Zoom website as well app. Upon execution of malicious “Zoom.exe”, it drops “Decoder.exe” which acts as a downloader to download additional payloads (RAT and Information Stealer), and the legitimate zoom app setup “ZOOMIN~1.EXE” to install the zoom app. The injected MSBuild.exe also downloads DLLs related to information stealers Vidar.
Usage of impersonated popular web application download pages in cyber-attack is not a new tactic but using the most downloaded application like Zoom to distribute malware is a dangerous move by threat actors indicating their intention of compromising a large number of systems worldwide. Based on their association with the ransomware group it is an even more worrying factor that compromised systems can be potential ransomware victims.
| Tactic | Technique |
|---|---|
| TA0002: Execution | T1059: Command and Scripting Interpreter T1204: User Execution |
| TA0003: Persistence | T1546: Event Triggered Execution |
| TA0004: Privilege Escalation | T1546: Event Triggered Execution |
| TA0005: Defense Evasion | T1553: Subvert Trust Controls |
| TA0006: Credential Access | T1555: Credentials from Password Stores T1539: Steal Web Session Cookie T1552: Unsecured Credentials |
| TA0007: Discovery | T1012: Query Registry T1518: Software Discovery T1082: System Information Discovery |
| TA0009: Collection | T1114: Email Collection |
| Type | IOC |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | b76cad93d0501d69746c84db3f7bfc158968900c2e472121019efe5d234ffa34 |
| MD5 | 19AFF3D6ED110A9037AFF507CAC4077F |
| MD5 | 98C8C28B790BBCE2BC2F20CC8FF2BD8E |
| MD5 | 21ABAC012CAA151DA5ED7C760198FAC6 |
| URL | http://116.202.179.139 |
| URL | http://193.106.191.223 |
| IP | 92.53.96.41 |
| IP | 5.101.159.26 |
| IP | 87.236.16.226 |
| IP | 92.53.113.155 |
| IP | 92.53.114.144 |
| IP | 92.53.114.172 |
| IP | 79.124.78.206 |