



Attackers continue to leverage malware and phishing attacks to target organizations as these are the easiest and most widely used techniques that yield maximum results. Attackers are also enhancing their arsenal and using sophisticated techniques that evade detection by conventional security solutions.
With ransomware developers increasingly offering their malicious tools through renting or service models such as Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), cybercriminal groups are taking advantage to distribute the malware and carry out attacks for financial gains.
A new report highlights the Lazarus group’s most recent campaign against Japanese firms. The research report underlines the threat actor’s most formidable hacking techniques and notes the use of the VSingle HTTP bot as a primary vector. As part of the recent campaign, the malicious code is stealthily executed to initially embed itself onto a system and download obfuscation and exploitation software. Some versions of the bot also undertake DLL injection to hide their activity. The group also makes use of ValeforBeta, which works similarly to VSingle, to transmit system information, send, and download files. After successful infection of primary system processes, threat actors use tools viz – 3Proxy, Stunnel, and Plink – in this operation to relay communication with C2 server.
North Korea’s cyber-warfare is in sync with its military philosophy. Strong anti-Japanese sentiments are manifested in the activities of state-sponsored threat groups like Lazarus that are primarily tasked with four objectives:
1. Financial gain as a method of circumventing long-standing sanctions against the regime
2. Collect intelligence, exfiltrate data and Espionage
3. Propagate states’ geopolitical aspirations
4. Showcase capabilities that will astonish the world.
The recent attacks carried out against pharmaceutical companies that develop vaccines, including AstraZeneca possibly to disrupt vaccine distribution and manufacturing vaccine. The US Department of Justice has accused three North Korean military personnel of participating in several hacking campaigns organized by the Lazarus Group.
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has provided an Early Warning to the MoRTH (Ministry of Road Transport and Highways) regarding potential targeted intrusion activities directed towards the transportation industry with possible malicious intentions. The threat actors have reportedly used either spear phishing, Drive via Download, or exploited known vulnerabilities present in public-facing applications as an initial entry mode to compromise the enterprise network. Cert-In also urged organizations to monitor and examine their network perimeter logs (firewall, proxy, etc.) particularly with a curated list of Indicators of Compromise for this campaign as provided by them.
Two Polish government websites were hacked to spread false information about a non-existent radioactive threat. A suspected Russian originating cyberattack led to the Health Ministry and National Atomic Energy Agency of Poland’s websites being hacked. In the era of ‘fake news’, public opinion can be drastically altered or reinforced with fictitious ‘news’ reporting. To counter this menace, the flow of information must be strictly monitored.
British newspapers claimed that the Ministry of Defence academy was the victim of a major cyberattack. China and Russian state-sponsored hackers are suspected to be behind this cyberattack. State-sponsored groups from Russia and China continually challenge the existing order without prompting direct conflict, operating in the expanding grey-zone between war and peacetime. The conflict is leading to a new attack surface over the wire, threatening the global interests of the targeted country.
KRD Trucking company based out of Chicago, US, is suspected to be targeted by DopplePaymer Ransomware Operators. The exfiltrated data may include confidential and business-critical data such as agreement details, transportation plan, specification, audit details. Threat actors are observed targeting less secured systems of suppliers, vendors, and partners for making inroads into the primary target’s infrastructure. Further, compromised systems and stolen information may also be used for extortion and tailored attacks on the organization.
The following screenshots were observed published in one of the dark web forums:

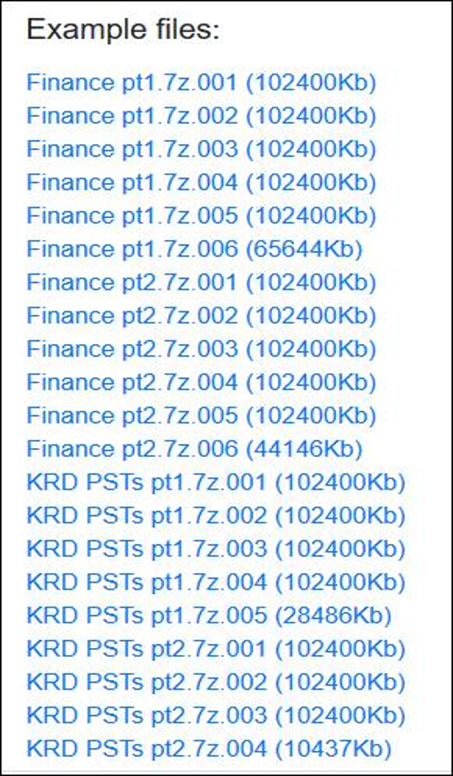
Ransomware or other forms of extortion represent the biggest cybersecurity threat for organizations. New variants of ransomware, as well as data leak sites (which host and/or advertise stolen information), are coming up every week, including some operated by the famous ransomware operators like Maze, Conti, DoppelPaymer, Sodinokibi, etc. Organizations face the risk of having sensitive data leaked to the public via these data leak sites along with the already tense situation involving encrypted files and locked systems.
REvil ransomware has a new technique that can encrypt files in Windows Safe Mode to evade detection by security software. In the new sample of the REvil ransomware discovered by security researchers, a new -smode command-line argument was added that compels the computer to reboot into Safe Mode before encrypting a device. The ransomware will forcefully reboot Windows which cannot be stopped by the user. Right before the process exits, the ransomware creates an additional RunOnce autorun named ‘AstraZeneca’. After the system restarts, the device will start up in Safe Mode with Networking, and the user will be advised to log into Windows. Once they login, the ransomware will be executed without the -smode argument so that it begins to encrypt the files on the device.
The motivation of the latest technique used by REvil ransomware operators is that most traditional antivirus software does not run in Windows Safe Mode, a Windows state meant for debugging and recovering a corrupt operating system. The REvil ransomware threat group has asserted that they successfully attacked multiple organizations spread across industries from Africa, Europe, Mexico & the US in the last two weeks. Initial investigation reveals that attacks were launched immediately after an extensive and well-planned drive-by-download campaign, which was launched in late December 2020.
Red Hat has released its security update for Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 7.3 for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. Multiple bugs and security fixes were addressed in this security advisory.
Cybercriminals continue to adopt new attack methods that exploit the vulnerabilities presented by the ever-increasing adoption of digital technologies.
The threat actor released a sample of thousands of records containing personal information such as Email address, Cell phone, Address, etc. Unlike other data leaks where threat actors often exploit the weakness in the system to exfiltrate unauthorized data, this threat actor claims to have secured access to the database physically.
The following screenshots were observed published in one of the underground forums:
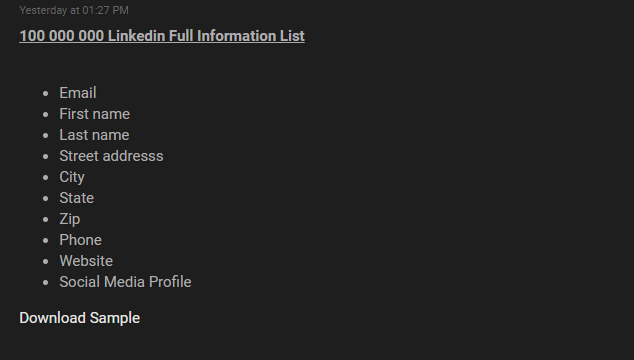
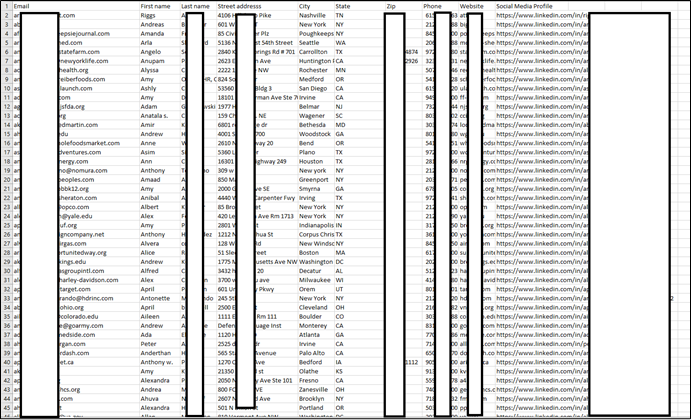
The leaked database includes personal details of major firms. The leaked user details are likely to be used by other threat actors to perform social engineering attacks.
The following screenshots were observed published in one of the underground forums:
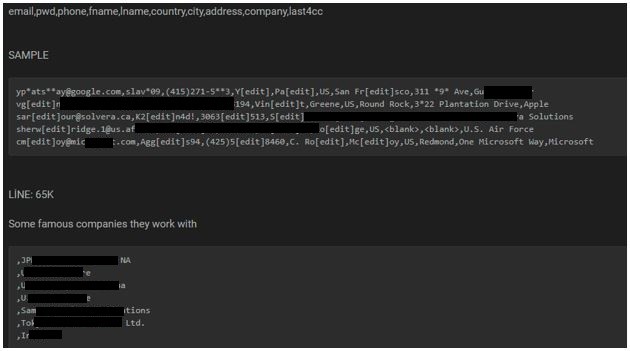
Organizations are required to take appropriate security measures to protect such critical data as it is one of the major treasure troves for hackers if they get access to them.