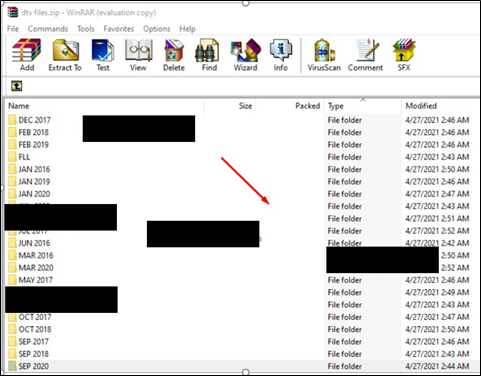
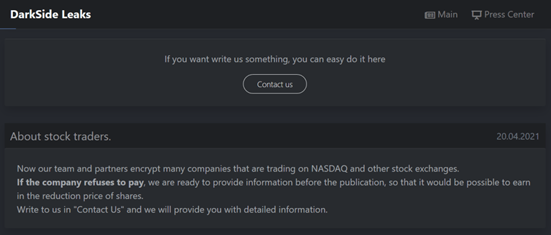
The relatively new RaaS (ransomware-as-a-service) gang – ‘DarkSide’ – is enhancing extortion tactics with a new technique aimed at companies that are listed on NASDAQ or other stock markets. The Darkside ransomware gang announced on their dark web portal that they can influence the stock prices of its victims by releasing sensitive information on their portal. While the offering will allow certain traders to make a profit from falling prices, the announcement is also a tactic to extort ransom from the victims as the negative press can impact the valuation of the company.
China-linked APT Naikon leveraged a new backdoor dubbed ‘RainyDay’ in multiple cyber-espionage operations targeting military organizations in Asia. Organizations targeted by the group were in multiple countries around the South China Sea, including the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, and Thailand.
The RainyDay backdoor helps the operators to perform reconnaissance on the infected machines, install scanners, execute tools for password dumping, deploy reverse proxies, lateral movement on the victim’s network, and achieve persistence.
Naikon made copious use of DLL hijacking to execute the malicious code. While investigating sideloading techniques, researchers uncovered a long-running campaign associated with the Naikon cyber-espionage group.
The Naikon APT group mainly focuses on high-profile organizations, including government entities and military organizations. To evade detection, the APT would mimic legitimate software. The motive of the attacks is espionage and data exfiltration, and the group continues to focus on Southeast Asian targets.
As per CISA, the Cozy Bear hacking group is continuing to target government networks, think tank and policy analysis organizations, and information technology companies. They are gathering intelligence and proprietary information.
According to the agency, the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) will continue to seek intelligence from the U.S. and foreign entities through cyber exploitation, using a range of initial exploitation techniques that vary in sophistication, coupled with stealthy intrusion tradecraft within compromised networks. Password spraying, leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities, and WELLMESS malware are among Cozy Bear’s TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures) highlighted in a joint advisory published by the government agencies.
Researchers highlighted that Cozy Bear’s behavior is not easy to monitor in comparison with other Russian government-linked hacking groups as they deploy rather sophisticated evasion techniques.
The little-seen botnet dubbed Prometei is borrowing TTPs from advanced persistent threat (APT). The malware is observed exploiting two of the Microsoft Exchange vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-27065) collectively known as ProxyLogon associated with the HAFNIUM attacks, malware deployment, credential harvesting, and more. The highly complex and sophisticated Prometei is a modular and multi-stage cryptocurrency botnet known to have Windows-based and Linux-Unix-based versions. To achieve their objective of mining Monero coins, it uses different techniques and tools, ranging from Mimikatz to SMB and RDP exploits, and other tools to propagate across the network. Researchers highlight that it has a resilient command and control Infrastructure comprising of a minimum of four different servers.
While the current cyber-attack trend is plagued with ransomware attacks and big-game hunting making the headlines, there are adversaries such as Prometei that use less intrusive ways to monetize their efforts. The researchers highlight that the Prometei group is financially motivated, and the operators are Russian-speaking individuals. But it does not appear to be backed by a nation-state.
According to Microsoft, cryptocurrency miners are usually a low-level security priority for most organizations. Organizations typically associate cryptocurrency miners with petty cybercriminals, and not sophisticated activities involving more serious players. In this case, the group has shown APT-like techniques, adding modules to expand their capabilities easily, and may potentially shift to more destructive objectives other than just mining Monero.
Summary: Researchers privately reported a flaw in macOS Catalina 10.15 and macOS Big Sur 11.3 in March 2021 tracked as CVE-2021-30657. This vulnerability is a logic issue that allows attackers to craft a macOS payload that is not checked by Gatekeeper.
Upon performing further root cause analysis of the vulnerability, researchers noticed a variant of Shlayer adware dropper was utilized. Previous variants of this malware are known to spread via poisoned search engine results. Once compromised, users are redirected to a new webpage asking them to download an application that looks similar to a real alert to update out-of-date software.
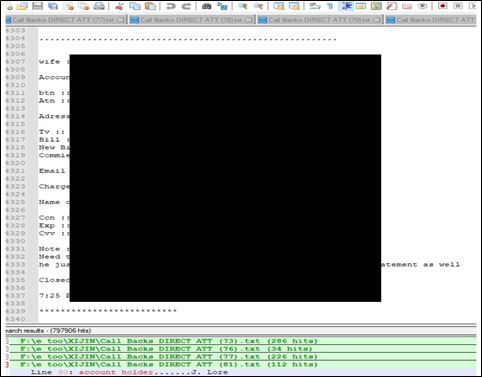
An unknown threat actor in an underground forum claims to have 800K users of AT&T and its subsidiary DIRECTV for sale. The leaked data include payment details, SSN (Social Security Number), address and phone numbers of impacted users. The threat actor is suspected to have collected logs of almost 10 years.
The following screenshots are related to the data leak: