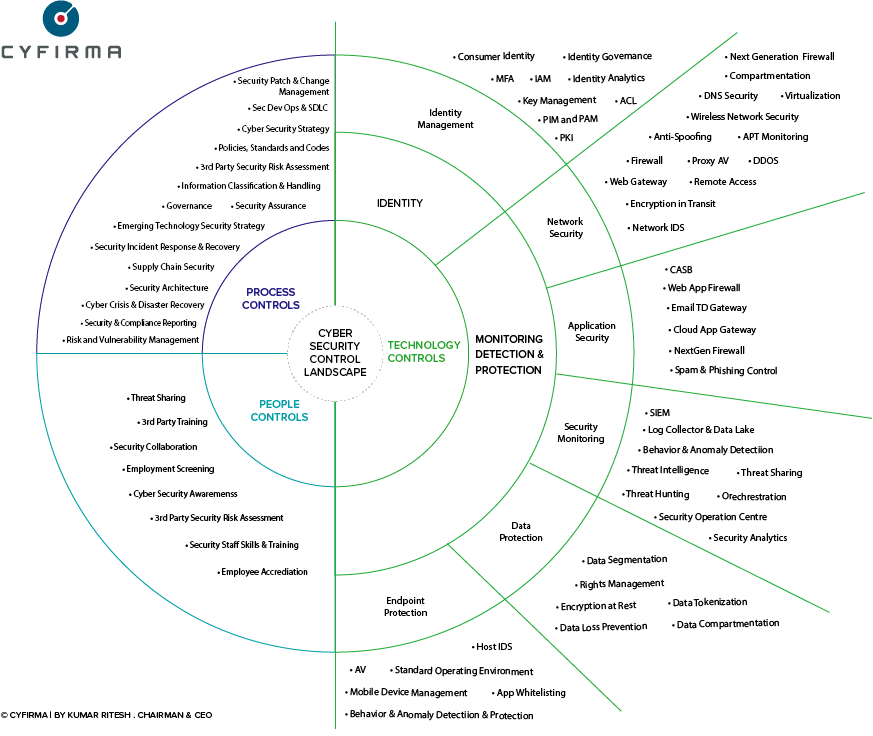
Effective consumption of Cyber Threat Intelligence plays an important role in the integration of threat intelligence program into an organization. To better prepare and protect against imminent cyber-attacks, organizations need to look at the application of threat intelligence to its strategy, governance, process, procedure, controls, and people.
Here is our attempt to define how Cyber Threat Intelligence should be applied and processed at THREE levels i.e. Strategic, Management, and Tactical.
For each level of intelligence, we have defined:
Time Horizon: Minimum review frequency
Consumer: Who should consume threat intelligence within an organization
Impact: Which elements of a process should be reviewed based on threat intelligence
Decision Point: What should trigger the review process
Interrogatives: Which level of threat intelligence provides answers to who, why what, when and how
Cyber Kill Chain: Narratives of each level of threat intelligence mapped to cyber kill chain
THREE level of Cyber Threat Intelligence:
Strategic: Risk-weighted threat intelligence applied to an organization’s overall business strategy enhancing its ability to proactively and continuously optimize the security posture based on its risk profile
Strategic intelligence should enable organizations to perform:
・ Identification of active and imminent threats, risks to the organization’s industry and brand
・ Determination of cyber risk profile and mitigation actions
・ Prioritization of cybersecurity investments and initiatives based on risk to critical people, processes and technologies
・ Qualification of cybersecurity risks relevant to the organization
・ Optimization and maintenance of the organization’s security posture
Management: Integrate insights on threat actor campaigns, attack mechanisms, and tools into the organization’s internal policy/processes for Cyber incident response, patch management, configuration management, release management, etc.
Management intelligence should enable organizations to perform:
・ Implement reliable and effective decisions for security processes, policies, and response
・ Assess the organization’s attack surface, threat, and vulnerabilities
・ Improve and maintain the efficacy of security controls
・ Updates to the organization’s overall risk register, including risk prioritization
・ Update information security compliance matrix based on threat actor profile, method, and activities
Tactical: Proactively respond to cyber threats, support detection and response to improve organization’s cybersecurity posture by using malicious IP, malware signatures & mutex, phishing domains, botnet command and control centers
Tactical intelligence should enable organizations to perform:
・ Formation of correct rules and policies to blacklist, detect and restrict malicious traffic
・ Detect infiltration and system infection
・ Detect, contain and remediate threats
・ Prevent phishing emails from reaching end-users
・ Protection against sensitive data leak
・ Application whitelisting/blacklisting
・ Real-time updating of AV malware signatures
・ File integrity, desktop/endpoint monitoring